|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
The term AI (Artificial Intelligence) was first coined by John McCarthy in 1956 at a conference in the US. But, what does AI mean in the real sense? AI is developing a smart integrated system or a machine that can think and learn like a human brain. When a task is assigned, an AI-based system/machine will analyze the problem. It understands the possible outcomes and provides an optimal solution, that is close to human thinking.
For a clear understanding of the term AI, let’s consider an example from the movie ‘Real Steel’ released in the year 2011. A robot named ‘ATOM’, in this movie was programmed with shadow function technology. Using this technique the bot can mimic human actions. The trainer uses this technique to his advantage to win the ‘bot boxing championship’.
Real-life examples of AI include Google maps, and ride-sharing apps like Uber, Ola, etc.
During the period of 1990, the term Machine Learning was introduced. Because the industries using AI had few limitations. like-
- Statistics: How to efficiently train large complex models?
- Computer Science & AI systems: How to train more robust versions of AI?
- Neuroscience: How to design artificial operational models of the Brain?
What is Machine Learning?
In Machine Learning, the machines are coded in the form of algorithms, which help the machine to understand, decode, analyze and perform the assigned tasks. In the case of unmatched algorithms, the machine denies completing the assigned task. The new data has to be programmed and analyzed by the machine, in order to perform future tasks. The human set of instructions is required to guide the machine while performing a task.
What are Algorithms?
Algorithms are the set rules/mathematical calculation techniques/problem-solving operations, that have to be followed by a machine while solving a problem
Let us understand Machine-Learning by an example:
If we ask a machine to draw a line that divides blue dots and red dots in the following graph. And the instruction was given to minimize the number of errors to obtain an optimal solution.
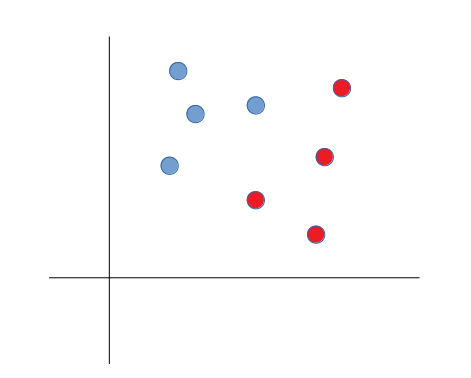
The machine analyzes the information and performs several trials to avoid maximum errors.
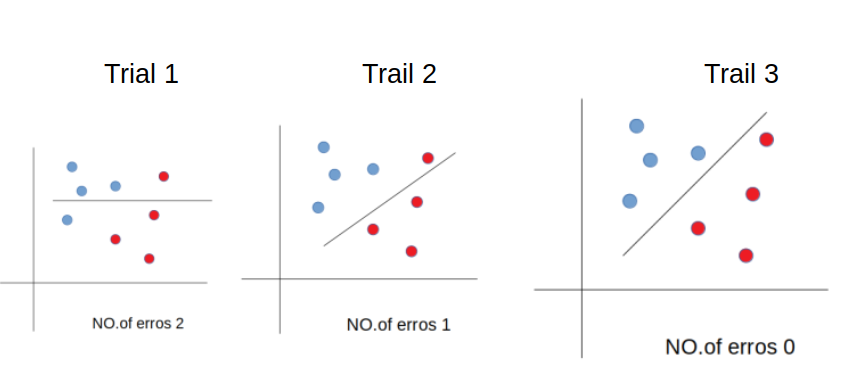
After two trials, in 3rd-trial the machine finds the graph with 0 errors, hence it considers it as an optimal solution and displays it to the user.
Real-life Machine Learning examples include Image Recognition, Speech Recognition, Medical Diagnosis, etc.
Types of Machine Learning used today:
- Supervised learning: Supervised learning is teaching a machine with explicitly labeled data by providing information regarding the input and outcome value. Example sales forecast
- Unsupervised learning: In unsupervised learning, the machine should process unlabelled data without the guidance of humans. The machine figures out the hidden patterns in the data and provides a possible outcome. For example a recommendation engine
- Reinforcement learning: In reinforcement learning the machine adopts established or encouraged patterns of data. By using a hit-and-trial concept to find a solution. This is leaving a machine in a typical situation. And the machine has to find the solution by increasing no.of hits, by interacting with the puzzle environment, and by adopting new changes. Example: self-driving cars
What is Deep Learning?
As years passed on, the amount of data that has to be processed increased gradually. To analyze these humongous datasets was not humans’ cup of tea. This is where Deep Learning came into the picture, Deep Learning uses neural networks to classify the data in structured and unstructured formats. It acts similarly to the neurons in the human brain to translate, analyze, understand, and progress the data.
The assigned task is analyzed by a neural input network, then communicated with interlinked hidden layers of metadata. Then networks send synapses from one layer to another, to obtain an optimal solution. it functions similarly to the neuron in the human brain.
As described above, Deep Learning functions on neural networks. These neural networks work similarly to neurons in the human brain, where it has three layers:
- – Input layer (acts as a dendrite of the neuron in the human brain)
- – Hidden layer (acts as a cell body of the neuron in the human brain)
- – Output layer (acts as an axon of the neuron in the human brain)
Example of Deep Learning: If you ask a voice assistant on your phone – Hey, Google, ‘ what is the best way from x to y location’?Voice assistant provides accurate information with the best optimal solution.
Before providing the solution, Voice Assistant runs a neural network diagnosis as explained below:
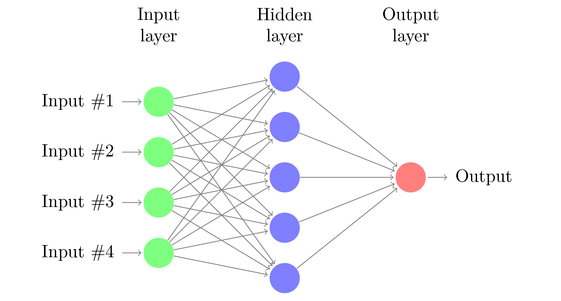
Image source: textample.com
The input layer of the neural network detects the location, distance, and travel time. Then the information is passed on to the hidden layers where the permutation and combinations of the information are performed. The best-detected route with minimum time will be projected out by the output layer.
Deep Learning examples that are in use: Fraud deduction, language recognition, and image processing.
If you need any help with idea validation, proof-of-concept, Data Science consulting, large-scale AI implementation, Big Data Engineering, or a creative solution for your AI, Machine Learning, and Deep Learning data. You are at the right place.
Talk to our experts
