|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
Understanding and leveraging different types of data analytics provides unique value to a business and improves organization-level operational capabilities respectively. In fact, what distinguishes the best data scientist or data analyst from the rest is their capability to identify the right kind of analytics that best fits the business needs to maximize outcomes. All types of analytics offer distinct insights. And in this article, we will explore the five different types of data analytics and their prominence in our business.
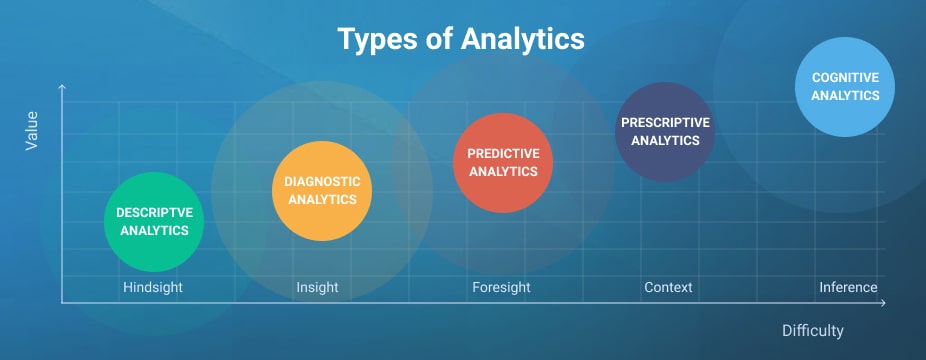
Five Types Of Data Analytics:
Choosing the right forms of data analytics can make the most of the unstructured or structured data you own. Discover five different forms of data analytics below;
1. Descriptive Analytics
90% of organizations around the world use descriptive analytics. It is the simplest class of analytics that allows you to constrict big data into smaller units to drive more incisive insights. It is a common tool leveraged today to drive important information from social and detailed media tools and websites. Leveraging descriptive analytics allows businesses to decode the inner context and reasons behind the previous success or failure.
Descriptive analytics help in extracting the utmost value through data mining to build and experience a business intelligence system that analyzes real-time and historical data to extract insights for the future approach. Examples of descriptive analytics include generating financial or sales reports.
2. Diagnostic Analytics
Diagnostic analytics is the second form of data analytics that helps the business in solving critical challenges by answering if something is happening, then why is it happening, and the root cause behind that. Diagnostic analytics plays its part when a business with business intelligence dashboards wants to drill down inside the data to find the reasons or factors that affect the industry. Integrating diagnostic and descriptive analytics helps businesses find relations and architecture of the data to make a quick comparison to build the most reliable data-based decision model.
An example of diagnostic analytics includes the HR department analyzing the applicant’s data sets.
3. Predictive Analytics
It is always fascinating to forecast the future, predict market trends, changing customer behaviors, and competitor analysis to optimize and build state-of-the-art strategies to maximize business outcomes. Predictive analytics is all about forecasting. Businesses utilize the insights driven by descriptive and diagnostic analytics and other historical data sets available to build a recommendation-based model by leveraging advanced statistical and machine learning models.
For instance, leveraging predictive analytical models in healthcare can identify if a person is susceptible to a heart attack or not by analyzing a patient’s past health records and general demographics. Similarly, predictive analytics can be leveraged to design a campaign based on the purchase behavior of consumers at different points in time in the past.
4. Prescriptive Analytics
Prescriptive analytics is the next step after predictive analytics that helps businesses in creating prescriptions to solve business problems based on the derived factors from data. While analyzing big data it is always uncertain to predict the most reliable inputs and highlight why those problems occurred. And it’s where prescriptive analytics comes into play.
Prescriptive analytics advises businesses on all possible outcomes and results in actions that are likely to maximize the business outputs. Prescriptive analytics can be defined as a business optimization data analytics process that provides insights on “ what should a business do” to solve a problem. This technique allows businesses to make informed decisions during uncertain times.
Examples of prescriptive analytics include marketing and business cycle reports.
5. Cognitive Analytics
Cognitive analytics is the most advanced form of analytics that combines a number of intelligent technologies like artificial intelligence, machine learning algorithms, deep learning models, and more to process the information and draw inferences from existing data and patterns, to derive conclusions. These findings are further added to the knowledge base for future interferences, and the self-learning feedback loop mirror human thinking to make cognitive applications smarter and more effective over time.
Examples of cognitive analytics include processing massive parallel/undistributed data (such as call center conversation logs) computing to derive insights.
These are different types of analytics and we hope you understood their importance for your business to boost your growth and increase your market presence. If you resonate with our article please share your thoughts with us.
If you need any help with idea validation, proof-of-concept, Data Science consulting, large-scale AI implementation, Big Data Engineering, or a creative solution for your Data. You are at the right place.
Talk to our experts
1 Comment
A great website with interesting and unique material what else would you need.