|
Getting your Trinity Audio player ready...
|
In today’s digital landscape, Conversational AI is revolutionizing the way we interact with technology, offering users a seamless and intuitive experience. Its integration into our lives offers a seamless and intuitive experience, enabled by the power of Large Language Models (LLMs).
Conversational User Interfaces
Conversational AI is poised to revolutionize the way we interact with technology. By using natural language to communicate with our devices, we can bypass the complex interfaces and artificial elements that have become commonplace in UI design.
Conversational User Interfaces (UIs) may not be the latest buzz, as we’ve witnessed the emergence of interactive voice response systems (IVRs) and chatbots since the 1990s. However, it’s crucial to understand that the landscape has evolved. In the pre-LLM era, these systems relied heavily on rule-based structures, keywords, and predefined conversational patterns. They were confined to specific, pre-defined domains, and any attempt to venture beyond these boundaries often led to dead ends and user frustration. These systems, while holding potential, were laden with points of failure, deterring users from returning. An example dialogue perfectly illustrates this scenario, with a user’s attempt to order concert tickets leading to disappointment.
Scenario: A customer is trying to book a flight online.
Traditional UI: The customer clicks on the “Book a flight" link and is taken to a page with a complex form to fill out. They start filling out the form, but they get an error message when they try to submit it. They try again, but they get the same error message. They start to get frustrated and give up.
Conversational AI: The customer opens their virtual assistant and says, “I need to book a flight."
The virtual assistant asks the customer for their travel dates and destination. The customer provides this information and the virtual assistant starts searching for flights. The virtual assistant finds a few flights that meet the customer’s criteria and presents them to the customer.
The customer selects a flight and the virtual assistant books it for them. The virtual assistant also sends the customer a confirmation email with their flight details.
In the above example, the conversational AI system provided a much more seamless and user-friendly experience than the traditional UI. The customer does not have to fill out any forms or navigate through any complex menus. They can simply tell the virtual assistant what they need and it takes care of everything for them.
As an enabling technology, LLMs have propelled conversational interfaces to new heights, enhancing the quality and overall user satisfaction. Conversational systems now possess broader world knowledge, linguistic competence, and conversational ability. The integration with pre-trained models has shortened development timelines significantly, eliminating the need for laborious rule compilation, keyword cataloging, and dialogue flow creation. This transformation allows for more efficient and user-friendly conversational systems.
Data and Conversations
The journey from language generation to understanding and participating in nuanced conversations is a fascinating endeavor in terms of conversational AI. Large Language Models (LLMs) are the cornerstone, originally designed to generate text tokens, which later evolve into coherent narratives. However, bridging the gap between language generation and human-like conversations is no small feat. Let’s explore the intricacies of conversational design and the role of fine-tuning data to make this transition smoother.
-
Understanding Conversational and Communicative Intent
Human conversation flows naturally, driven by specific communicative intents. We use language to convey information, socialize, or request actions, each with its unique characteristics. While LLMs can handle the first two intents with relative ease, the third poses more significant challenges. This involves not only structuring information coherently but also imbuing the conversation with the appropriate emotional tone, considering factors like formality, creativity, humor, and more. For instance:
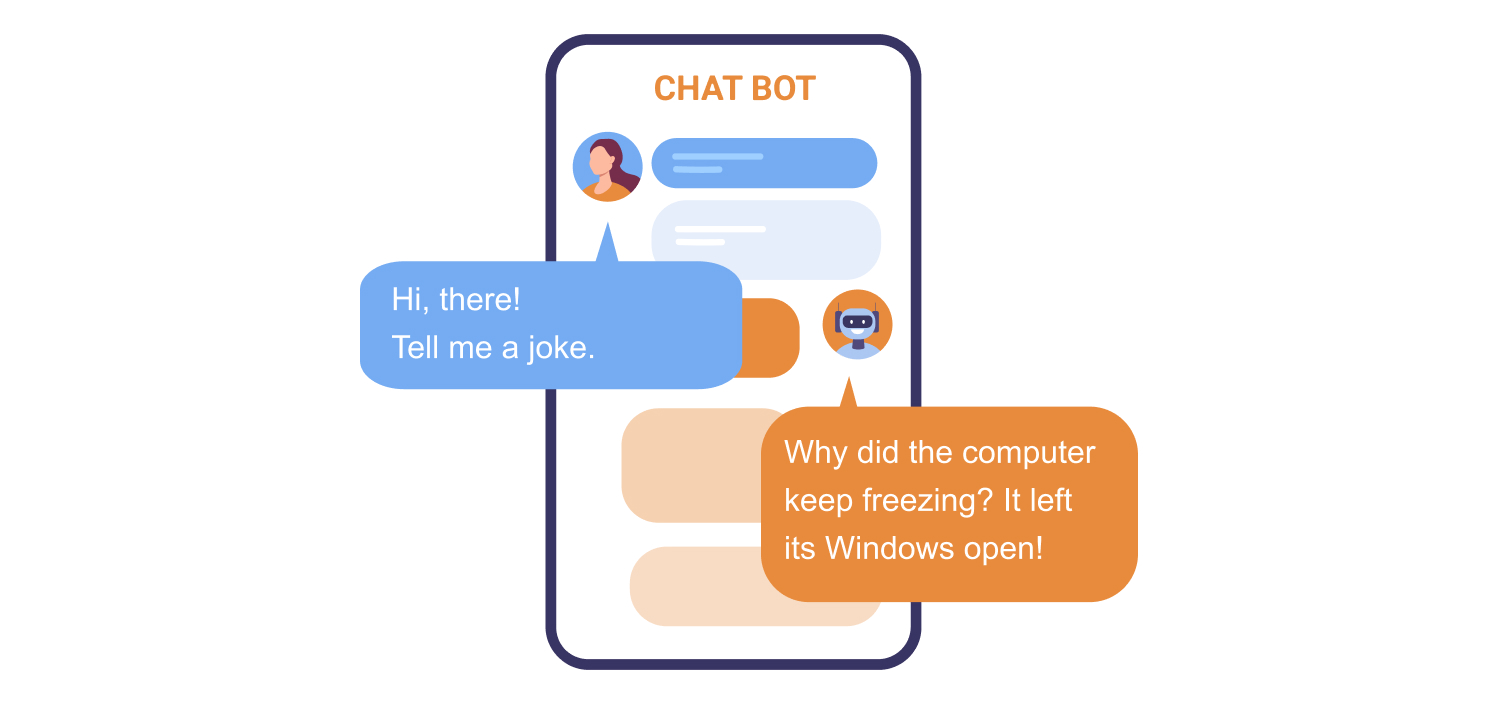
-
Building the Right Dataset
Fine-tuning begins with assembling a dataset that closely mimics real-world conversational data. It should embrace dialogues, reflect domain-specific knowledge if your virtual assistant operates in a particular field, and include a variety of recurring user flows and requests. This diverse dataset lays the foundation for teaching your AI the art of conversation. Imagine this scenario:
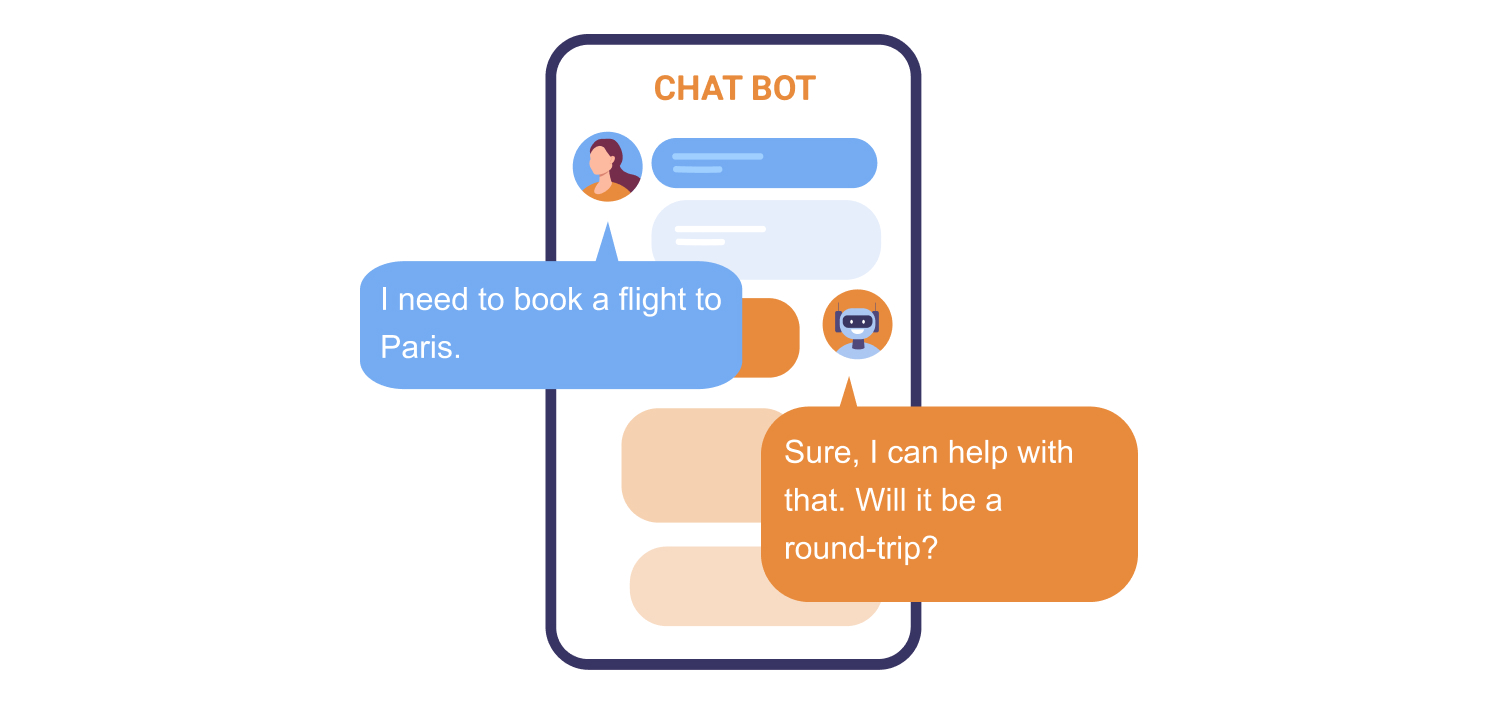
-
Fine-tuning the Conversation Skills
For fine-tuning the conversations, you’ll need the collected fine-tuned data and a pre-trained LLM. These LLMs come with extensive language and world knowledge. Fine-tuning is about teaching them the nuances of conversation. This involves defining a specific conversational AI task, gathering data, and iteratively fine-tuning the model to generate text that aligns with the targets. Here’s an example:
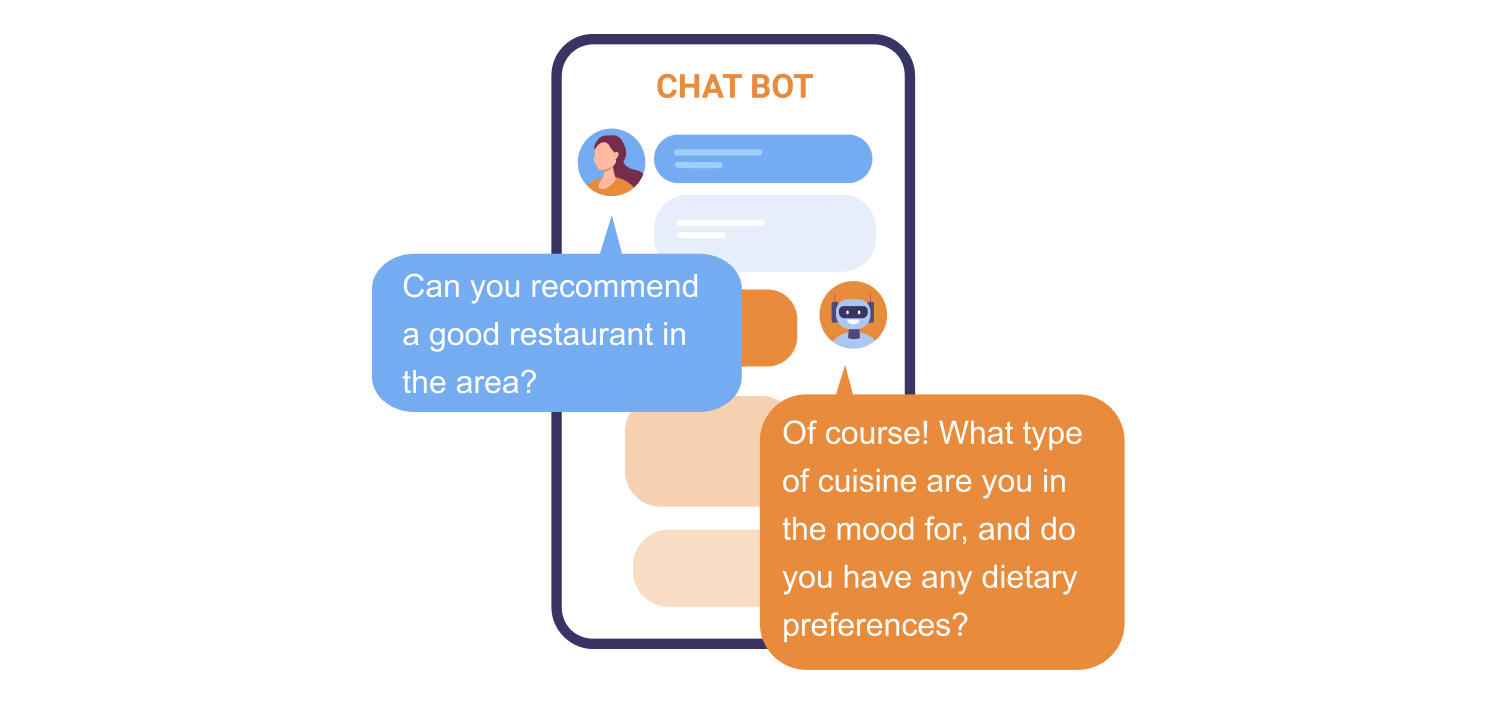
-
Maintaining Memory and Context Awareness
Effective conversations require context awareness. Your conversational assistant should not only understand the current conversation but also remember past interactions. Coreference resolution, or understanding pronoun references, is crucial. Humans intuitively grasp these contextual cues, which virtual assistants need to learn. Context awareness avoids repetitive questions about personal details and enhances user experience.
What is Prompt Engineering?
Prompt engineering is a pivotal aspect of harnessing the full potential of Large Language Models (LLMs) in Conversational AI. It plays a vital role in ensuring that LLMs provide contextually accurate and relevant responses. In essence, prompt engineering involves crafting specialized input prompts or queries to guide LLMs in generating desired outputs.
LLMs like ChatGPT are versatile tools, adept in multiple languages, and well-informed about an array of topics. However, they have their limits, particularly when it comes to recent events, confidential data, and the occasional generation of plausible-sounding but incorrect information, known as hallucinations. For data-driven roles, where precise, trustworthy insights are vital, LLMs may require support.
To overcome LLM limitations, prompt engineering plays a crucial role. Crafting more complex prompts and incorporating industry-specific documents and data can provide the necessary precision. While this approach enhances responses, it can lead to lengthy prompts and demands careful data selection.
The relevance of prompt engineering becomes evident when we consider the expansive knowledge and capabilities of LLMs. These models are proficient in understanding language and drawing from their extensive training data. However, to extract precise and contextually relevant information from LLMs, prompt engineering acts as the bridge.
For instance, let’s delve into a scenario where you seek specific insights from an LLM:
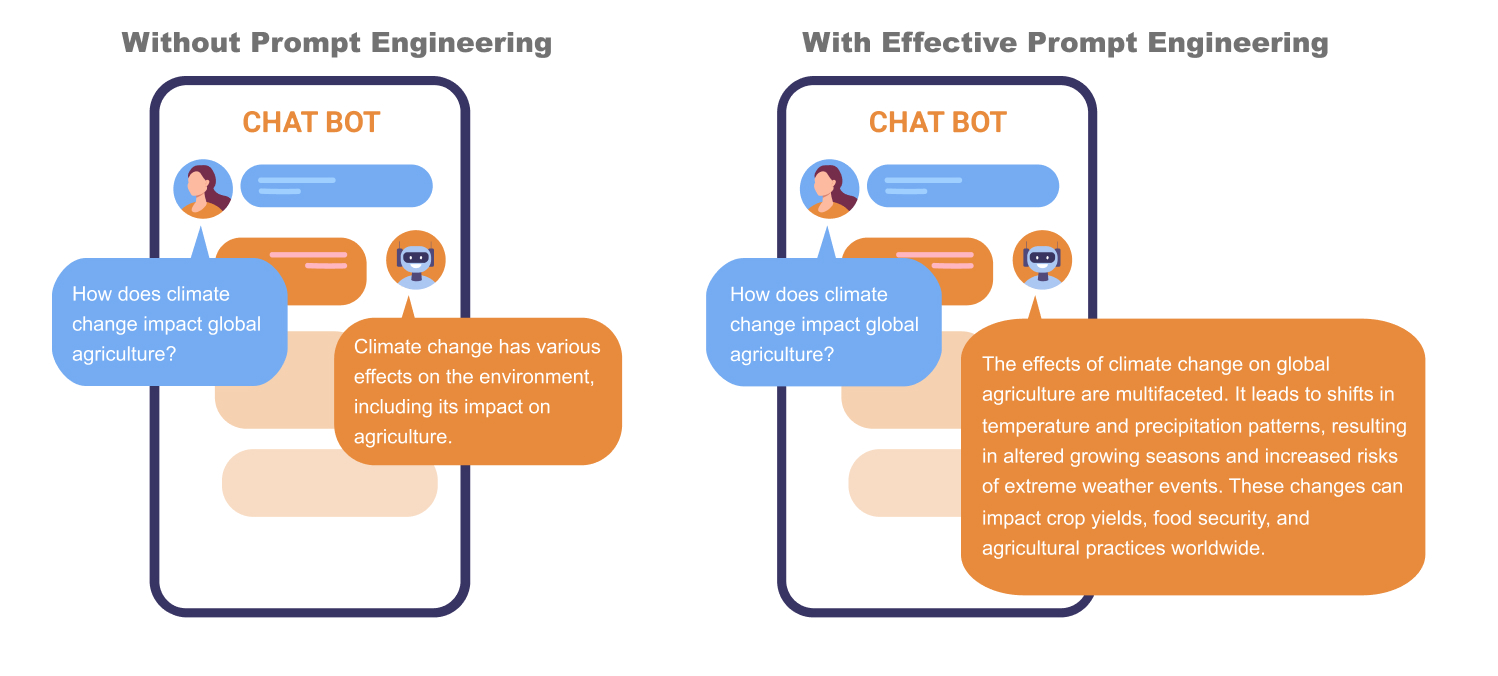
User: Can you provide an in-depth analysis of quantum entanglement?
Without effective prompt engineering, the LLM might offer a broad overview, but it could miss the nuanced, detailed explanation you require.
On the other hand, with the right prompt engineering, the conversation might go like this:
As this example illustrates, prompt engineering guides the LLM to provide a more focused and contextually accurate response. It empowers users to extract specific, valuable insights from the wealth of knowledge that LLMs possess.
Incorporating prompt engineering is a valuable strategy for optimizing Conversational AI interactions. It ensures that users can make the most of LLMs’ capabilities and receive precise, contextually appropriate responses. Effective prompt engineering transforms conversations from broad overviews to insightful and focused exchanges, enriching the user experience.
The Art of Conversational Design
In the ever-evolving landscape of user interfaces, the rise of conversational interfaces introduces a profound shift in how users interact with technology. While the prospect of uniformity across applications may raise questions about the future of traditional User Experience (UX) design, it’s essential to emphasize that the role of UX designers is far from doomed. In fact, it’s undergoing a fascinating transformation.
Conversational design is the art of teaching Large Language Models (LLMs) to conduct conversations that are not just functional but also enjoyable, natural, and comfortable for users. It’s a creative endeavor that blends elements of human psychology, linguistics, and traditional UX design to shape the future of interactions. In this section, we will explore the fundamental aspects of conversational design that lead to a seamless and engaging user experience.
-
Choices in Building Conversational Systems: Voice, Chat, and Context
When embarking on the journey of conversational design, you encounter two fundamental choices: the medium of interaction, whether it’s voice, chat, or a combination of both, and the broader context within which your system operates.
Medium of Interaction: The decision to use voice, text-based chat, or a fusion of both hinges on your users’ preferences and the nature of your application. Voice interfaces offer a hands-free, convenient experience, while chat interfaces provide users with text-based interactions. Understanding your audience’s comfort and context is vital in making this choice.
Context of Your System: Consider the larger environment in which your conversational system operates. Is it a customer support chatbot, a voice assistant in a smart home, or an educational tool? The context influences the conversational design and the role your assistant plays.
-
Crafting Conversations and Defining Personality
Conversational design goes beyond the medium and context; it delves into the heart of user interactions: conversations. Here, we explore two essential aspects that shape the art of conversational design.
Designing Conversational Flow: Effective conversational design involves crafting intuitive dialogue flows. This requires an understanding of user intent and the ability to guide users seamlessly through interactions. Consider this scenario:
User: I’m planning a trip to Paris. Can you help me find the best places to visit?
A well-designed conversation would lead to a series of prompts that gather information about the user’s preferences, travel dates, and interests to provide tailored recommendations.
Defining the Assistant’s Personality: The personality of your conversational assistant plays a pivotal role in user engagement. It’s not just about delivering information; it’s about doing so in a way that aligns with your brand and resonates with users. Is your assistant formal, informal, informative, or playful? The personality shapes the user experience.
For instance, an educational chatbot might adopt an informative and professional tone:
On the other hand, a travel planning assistant might have a more friendly and conversational tone:
Conversational design is about infusing your assistant with a personality that resonates with your target audience. It’s the art of crafting interactions that not only provide information but also engage users on a human level.
Applications of Conversational AI at Scale
Conversational AI brings remarkable value across various domains. Let’s explore two prominent applications where it excels:
-
Elevating User Experience in Customer Support
In the realm of customer support and user-focused applications, the potential of Conversational AI truly shines. These applications cater to a broad user base, often fielding similar queries and requests. Companies that excel in customer support hold a significant informational advantage over their users, and harnessing this advantage can lead to a seamless and enjoyable user experience.
Consider the scenario of a busy online retail platform. Shoppers often require assistance, whether it’s tracking their orders, resolving issues, or seeking product recommendations. This platform recognizes that user satisfaction is paramount and leverages Conversational AI to provide a top-notch experience.
Streamlining Order Tracking
Imagine a frequent online shopper who loves exploring the latest trends. She orders items regularly but occasionally loses track of shipment details. Instead of navigating through the website’s interface, she engages with the virtual assistant using natural language. The assistant swiftly retrieves her order details and provides real-time updates. This convenience not only saves time but also enhances her overall shopping experience.
Personalized Product Recommendations
Our shopper has eclectic tastes, and the retail platform is well aware of her browsing history. With Conversational AI, the platform’s virtual assistant engages her in a friendly conversation. It asks about her style preferences, favorite brands, and the type of products she’s interested in. Based on this interaction, the assistant generates personalized product recommendations. Our shopper is thrilled to discover unique items that align with her taste, and her shopping journey becomes more enjoyable.
-
Unlocking Corporate Knowledge with Conversational AI
In the fast-paced world of modern business, companies amass a wealth of knowledge through years of operation. Yet, the challenge lies in effectively storing, managing, and accessing this valuable information. It often remains hidden within collaboration tools, internal wikis, and knowledge repositories, becoming a labyrinth of untapped potential. This underutilized knowledge can lead to chaos as employees come and go, leaving documentation incomplete and information scattered. Retrieving specific details becomes an arduous task, resulting in inefficiencies for knowledge workers.
Streamlining Internal Knowledge Retrieval
Imagine a dynamic tech company, known for its innovative products and solutions. Over time, it has accumulated a vast amount of data, from technical documentation to project insights. However, this information is dispersed across various platforms, making it challenging for employees to access the precise details they need.
To address this issue, the company introduces Conversational AI as a knowledge management solution. Now, employees can simply engage with the virtual assistant using natural language. They can ask questions about a wide range of topics, from troubleshooting a technical issue to finding the latest market research data.
The virtual assistant utilizes semantic search capabilities, seamlessly navigating the company’s internal data sources. It understands the context of the queries and retrieves relevant information, making knowledge retrieval a breeze. Employees no longer need to grapple with complex search queries or sift through numerous documents. Instead, they can focus on their specific information needs, confident that the virtual assistant will deliver accurate and timely responses.
Beyond these significant applications, the potential of Conversational AI extends to various domains, including telehealth, mental health assistance, and educational chatbots. These applications streamline user experiences, offering faster and more efficient interactions.
Transforming Conversational AI
A solid model paves the way for the success of any conversational AI. Let’s break down the key elements that shape this exciting landscape:
Data: Collect and annotate dialogue data to teach your virtual assistant valuable attributes like helpfulness and creativity.
Intelligence: Fine-tune your model, integrate real-time data, and build a robust memory. Add safeguards for uncharted territory.
Opportunity: Revolutionize customer service and tackle knowledge management complexities with the help of cutting-edge technology.
User Experience: Flexible interfaces, consistent personalities, context awareness, and cooperative interactions enhance the user experience.
In essence, Conversational AI is a game-changer, redefining interactions between humans and machines. Join us to explore its limitless potential.
Ready to unlock the future of Conversational AI? Contact us now!